What Is Allergy
An abnormal reaction, to normally harmless substances in the majority of the population, by the immune system, the bodies defence mechanism against foreign invaders, such as pathogens (the causes of infection). The substances that trigger allergy are called allergens. This includes pollens of grasses, trees and weeds, house dust mite, mould spores, animal danders, and certain foods. People prone to allergies are said to be allergic or atopic, sometimes referred to as Immediate Hypersensitivity or Type 1 allergy.

Although allergies can develop at any age, it is more common to be during childhood. The risk of developing allergies is usually genetic. It is related to family history of allergy. When neither parent is allergic, the chance for allergies is about 15%, one parent is allergic, the risk increases to 30% and if both are allergic, the risk is greater than 60%.
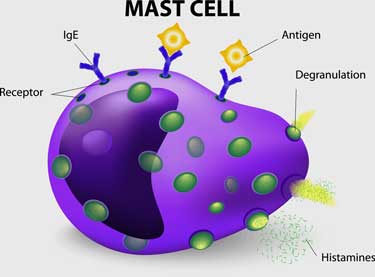
Allergens cause the production of immunoglobulin E (IgE), an antibody that all of us have in very small amounts. Allergic individuals produce IgE in significantly higher quantities. This antibody production evolved to help protect us from parasitic infestations but not to respond to allergens. When someone predisposed to allergy is exposed to an allergen, they produce specific IgE to it. This antibody then binds to certain cells in the body (Mast Cells) and on further exposure to the allergen there is a reaction between the bound antibody and allergenic proteins (a bridging reaction) resulting in the release (degranulation) of many substances, most notably histamine. The released histamine and other components cause inflammation resulting in the allergic response.
The allergic conditions include perennial and seasonal (Hay Fever) allergic rhinitis, asthma, allergic conjunctivitis, allergic eczema (atopic dermatitis), urticaria, and anaphylaxis (allergic shock). The symptoms of these can summarised as:
What Are The Symptoms Of Allergy?
Allergic rhinitis is the most common of the allergic diseases and refers to seasonal nasal symptoms (Hay Fever) that are due to the pollens of grasses, trees and weeds. Year round or perennial allergic rhinitis is usually due to indoor allergens, such as house dust mites, animal dander or moulds. Symptoms result from the inflammation of the tissues that line the inside of the nose (nasal mucosa) after allergens are inhaled. Adjacent areas, such as the ears, sinuses, and throat can also be involved. The most common symptoms include:
-
Runny nose
-
Stuffy nose
-
Sneezing
-
Nasal itching (rubbing)
-
Itchy ears and throat
-
Post nasal drip (throat clearing)
Asthma is a breathing problem that results from the inflammation and spasm of the lung’s air passages (bronchial tubes). The inflammation causes a narrowing of the air passages, which limits the flow of air into and out of the lungs. Asthma is most often, but not always, related to allergies. Common symptoms include:
-
Shortness of breath
-
Wheezing
-
Coughing
-
Chest tightness
Allergic conjunctivitis (often in combination with symptoms of allergic rhinitis) is inflammation of the membranes that cover the surface of the eyeball and the undersurface of the eyelid. The inflammation occurs a result of an allergic reaction and features:
-
Redness under the lids and of the eye overall
-
Watery, itchy eyes
-
Swelling of the membranes
Allergic eczema or atopic dermatitis is an allergic rash that is usually not caused by skin contact with an allergen and features the following symptoms:
-
Itching, redness, and or dryness of the skin
-
Rash on the face, especially children
-
Rash around the eyes, in the elbow creases, and behind the knees, especially in adults
Urticaria are skin reactions that appear as itchy swellings and can occur on any part of the body. It can be caused by an allergic reaction, such as to a food or medication, but they also may occur in non-allergic people. Typical urticaria symptoms are:
-
Raised red welts
-
Intense itching
Anaphylaxis or allergic shock is a life-threatening reaction that can affect a number of organs at the same time. It typically occurs when the allergen is eaten (for example, foods such as peanuts) or injected (for example, a bee sting). Allergic shock is caused by dilated and “leaky” blood vessels, which result in a drop in blood pressure. Some or all of the following symptoms may occur:
-
Urticaria or reddish discoloration of the skin
-
Nasal congestion
-
Swelling of the throat
-
Stomach pain, nausea, vomiting
-
Shortness of breath, wheezing
-
Low blood pressure or shock